Think You're in the Clear on Blood Pressure? Think Again
Think You're in the Clear on Blood Pressure? Think Again
By Unknown
Updated
5 minute read
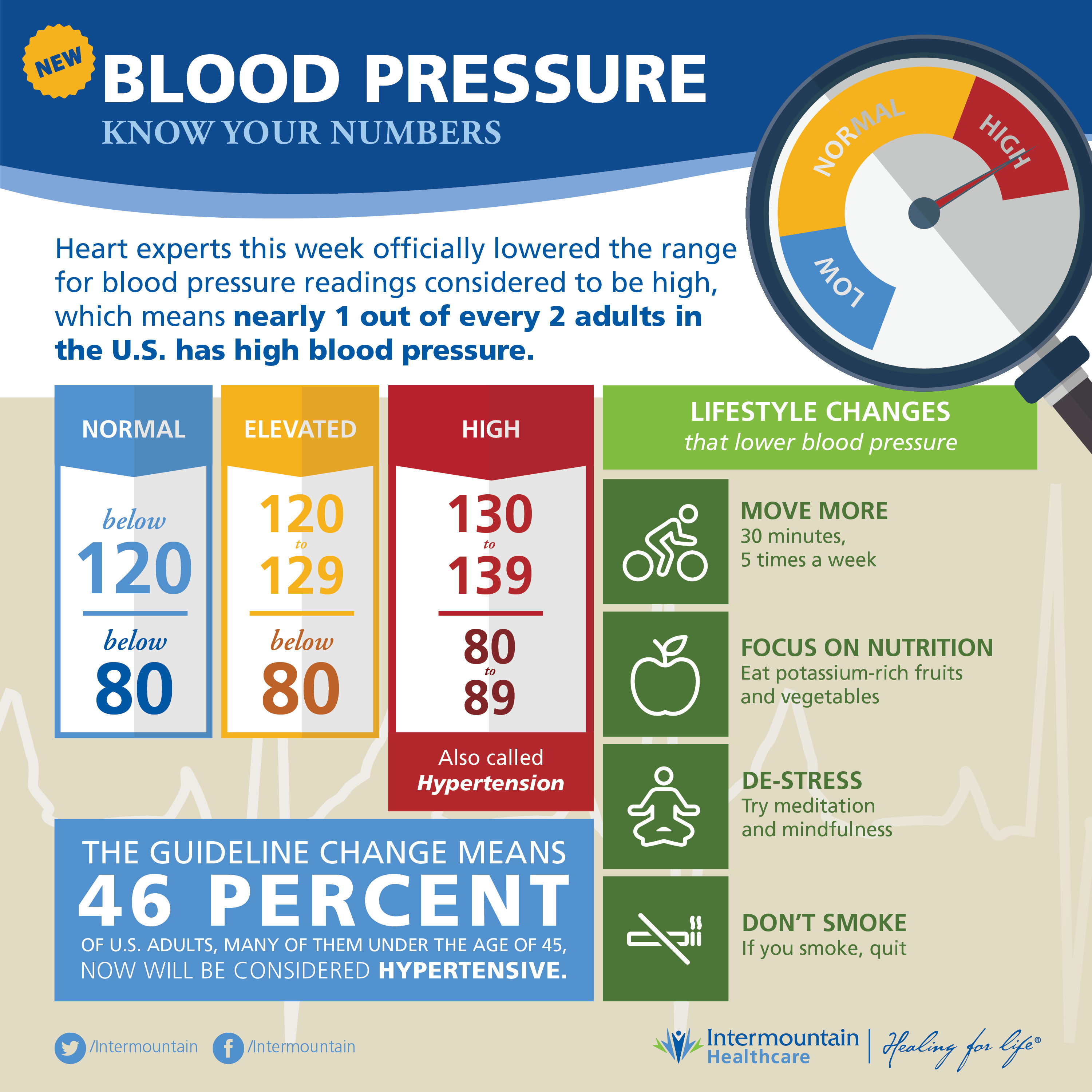
Heart experts this week officially lowered the range for blood pressure readings considered to be high, which means nearly one out of every two adults in the U.S. has high blood pressure — compared to one out of three under previous guidelines — and needs to work to bring it down.
At the 2017 Scientific Session of the American Heart Association, held this week in Southern California, the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and nine other groups announced that anyone with blood pressure readings higher than 130 over 80 will be considered to have high blood pressure (or hypertension). Previously, people weren’t considered to have high blood pressure until the top reading hit 140.
What's New With the Blood Pressure Guidelines?
According to the new guidelines, blood pressure of 120 over 80 is normal; anything between 120 and 129 over 80 is now considered elevated; 130 over 80 to 139 over 89 is now considered stage 1 hypertension; and anything 140 over 90 or above will be considered stage 2 hypertension. (See the attached CardioSmart infographic from the American College of Cardiology.) If blood pressure reaches 180 over 120 or higher, people will be considered to be in hypertensive crisis and need immediate treatment or hospitalization.
The guideline change means 46 percent of U.S. adults, many of them under the age of 45, now will be considered hypertensive. Under the previous guideline, 32 percent of U.S. adults had high blood pressure.
Why the Change?
Heart health experts tightened the guidelines in the hope that the millions of U.S. adults considered hypertensive, and their doctors, will address the deadly condition sooner.
Jeffrey L. Anderson, MD, cardiovascular researcher at the Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute, who was at the conference when the announcement was made, says this is the first update to the blood pressure guidelines in 14 years.
“There’s been a lot of new evidence come in since then,” he said, “and the evidence now is very strong that lesser elevations in blood pressure significantly impact cardiovascular risk.”
In an NBC News report, Robert M. Carey, MD, professor of medicine and dean emeritus at the University of Virginia and co-chair of the group that produced the new report, said: “We're recognizing that blood pressures that we in the past thought were normal or so-called pre-hypertensive actually placed the patient at significant risk for heart disease and death and disability. The risk hasn't changed. What's changed is our recognition of the risk.”
The report recommends that people 65 and older adopt the same blood pressure goal as younger patients, saying it can be lifesaving: “BP-lowering therapy is one of the few interventions shown to reduce mortality risk in frail older individuals.” Under the new classification, the total number of men and women age 65 to 74 with high blood pressure rates will increase by 13 percent and 12 percent, respectively.
What Should You do if Your Blood Pressure is Above the New Guideline?
In an interview with KSL Radio this week from the AHA’s scientific sessions in Anaheim, Intermountain’s Dr. Anderson suggests watching your blood pressure closely.
“I think you should start to worry if it’s over 120 and get on to lifestyle changes,” he said. “Certainly if it’s over 130, you ought to be working with your healthcare provider and your physician to make sure you’re going to get that down over the long term.”
Instead of recommending drug treatment right away, the organizations that issued the new guidelines hope that many people found with the early stages of the condition will be able to address it through lifestyle changes such as losing weight, improving their diet, getting more exercise, consuming less alcohol and sodium, and lowering stress.
Dr. Anderson agrees: “Diet and exercise can have a tremendous impact, so that’s the first place to start.”
Additional examples of blood-pressure lowering lifestyle changes are in the infographic above, courtesy of CardioSmart.)
“This is a wonderful advance to help all of us reduce the risk of stroke, heart attacks, and heart failure, which really are three out of the top five or six reasons that as we get older we have significant disability and mortality associated with our lifestyle,” said Dr. Anderson.
High blood pressure damages blood vessels and can lead to organ damage such as kidney and heart failure, as well as heart attacks and stroke. It’s one of the leading killers around the world as well as across the United States.
While people may be confused by the change, the heart experts said three years of reviewing the research showed that many fewer people die if high blood pressure is treated earlier.