Germ Profile
Also Known As: Common cold, conjunctivitis, tonsilitis, diarrhea, bronchiolitis
Germ Type: Virus
Season: Winter, spring, summer
Adenovirus refers to a group of common viruses that mostly affect younger children. Daycares and schools often have outbreaks of adenoviruses, which can cause respiratory symptoms (sinus or throat problems, cough) and gastrointestinal problems (diarrhea, vomiting). Illnesses are usually mild, but they can sometimes lead to serious problems — especially in babies.
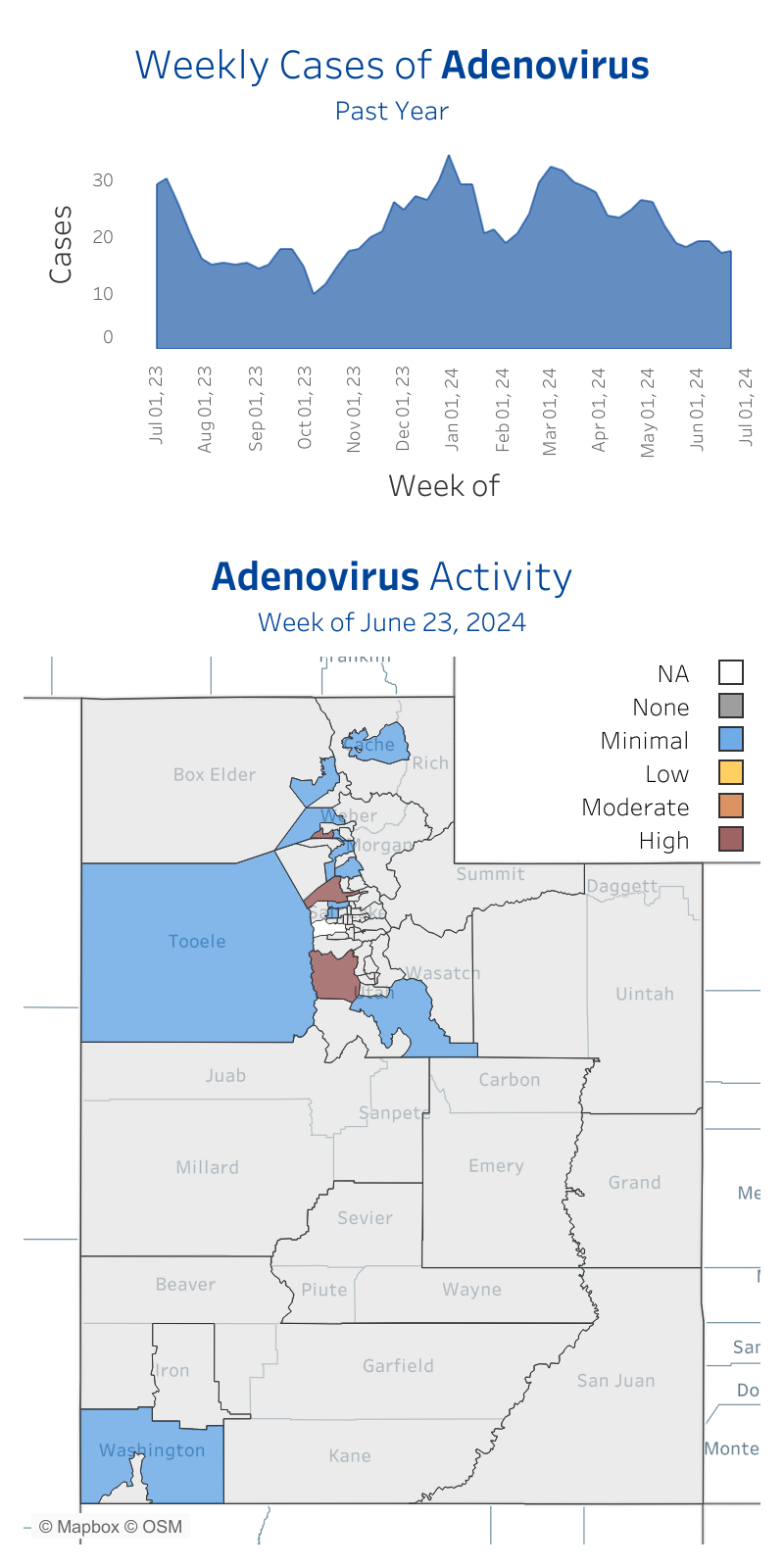
Seasonality
Adenovirus infections are seen year-round. In winter, spring, and early summer, respiratory symptoms are more common. Gastrointestinal symptoms are seen year round, mostly in children younger than 4.
Signs and Symptoms
Adenovirus can affect nearly every part of the body. Depending on the specific virus and the severity of infection, adenovirus can cause symptoms in the eyes (runny and red eyes), sinuses (stuffy or runny nose), throat (soreness), chest (cough, breathing problems), and stomach and intestines (diarrhea, vomiting, cramps). Adenovirus can also lead to ear infections and urinary tract infections.
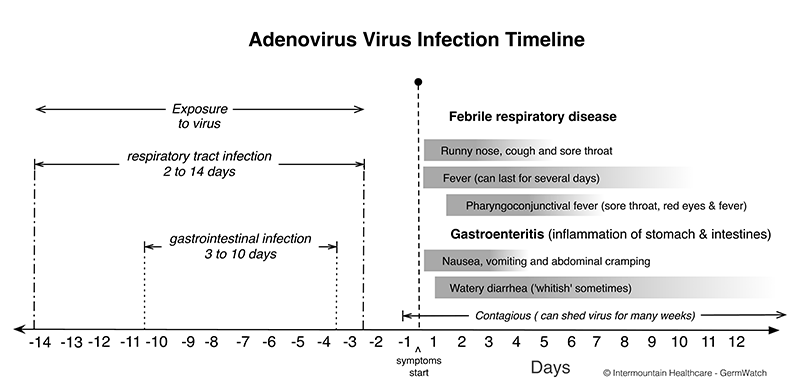
Infection Period
Symptoms of a respiratory adenovirus infection typically develop between 4 and 8 days after being exposed to (or infected with) the virus. With gastrointestinal illness, the range is 3 to 10 days.
How It's Spread
By the time they’re 10 years old, most people will have had at least one illness caused by adenovirus. It’s very contagious and spreads easily in close-contact settings such as daycares, schools, and summer camps. Different adenoviruses are spread in different ways:
- Adenoviruses causing respiratory infections are spread person-to-person via respiratory secretions – in other words, by coughs, sneezes, and mucus. The virus can also live on surfaces (tables, handrails, doorknobs, toys and so on).
- Adenoviruses causing GI symptoms can be spread by contact with fecal matter. (Poor hygiene after bathroom breaks or diaper changes is the big problem.)
Diagnosis and Treatment
Although tests can detect adenovirus, most diagnoses are made on the basis of symptoms. Treatment for adenovirus means managing symptoms until the infection clears. (There’s no commonly used treatment that acts on this group of viruses.)
What can I do today?
1) Practice prevention and stop the spread:
- Wash your hands often and well, and have children do the same. (Give special attention to post-potty and pre-meal hand washing.)
- Regularly wipe down tables, toys, and other objects and surfaces.
- Cover your sneezes and coughs.
- Use a tissue once, then throw it away and wash your hands.
2) Call your child’s doctor if you notice:
- Fast breathing (more than 40 times a minute) or very difficult breathing (retractions, or using the stomach muscles when breathing).
- Fever higher than 100.2°F in an infant 3 months or younger.
- Fever lasting longer than 3 days.
- Signs of dehydration (dry mouth and eyes, little urine, low energy).
- Eye swelling or redness that becomes worse or is painful.
- Any severe symptoms or symptoms that last longer than 7 days.
Related Conditions
Adenovirus
Disclaimer: The contents of this website are not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.